
Download PDF
Translations (PDF)
Keras enables fast experimentation with “neural networks”. It supports convolution networks (vision) and recurrent networks (text and time series). It provides the freedom to x work with JAX, Tensorflow, and Torch, plus the freedom to build models that can seamlessly move across these frameworks. keras3 provides easy access to the Keras vast API. It also makes getting started with Keras faster by automatically creating a working Python environment with all the needed libraries pre-installed.
keras_input() / keras_model(): Defines a Functional Model with inputs and outputs.
keras_model_sequential(): Define a Sequential Model composed of a linear stack of layers
Model(): Subclass the base Model class
summary(<model>): A summary of a Keras Model
plot(<model>) Plot the model. Needs graphviz to work: graphviz.gitlab.io/download
compile(): Configure aspects of the model such as optimizer, loss, metrics, weights and others.
fit(): Trains the model for a fixed number of dataset iterations (epochs)
evaluate(<model>): Returns the loss and metrics
predict(<model>, x): Generates predictions
Train image recognizer on MNIST data a.k.a. deep learning’s ‘hello world’ example
library(keras3)
# Input layer: use MNIST images
.[.[x_train, y_train], .[x_test, y_test]] <- dataset_mnist()
# Rescale and categorize
x_train <- x_train/255
x_test <- x_test/255
num_classes <- 10
y_train <- to_categorical(y_train, num_classes)
y_test <- to_categorical(y_test, num_classes)
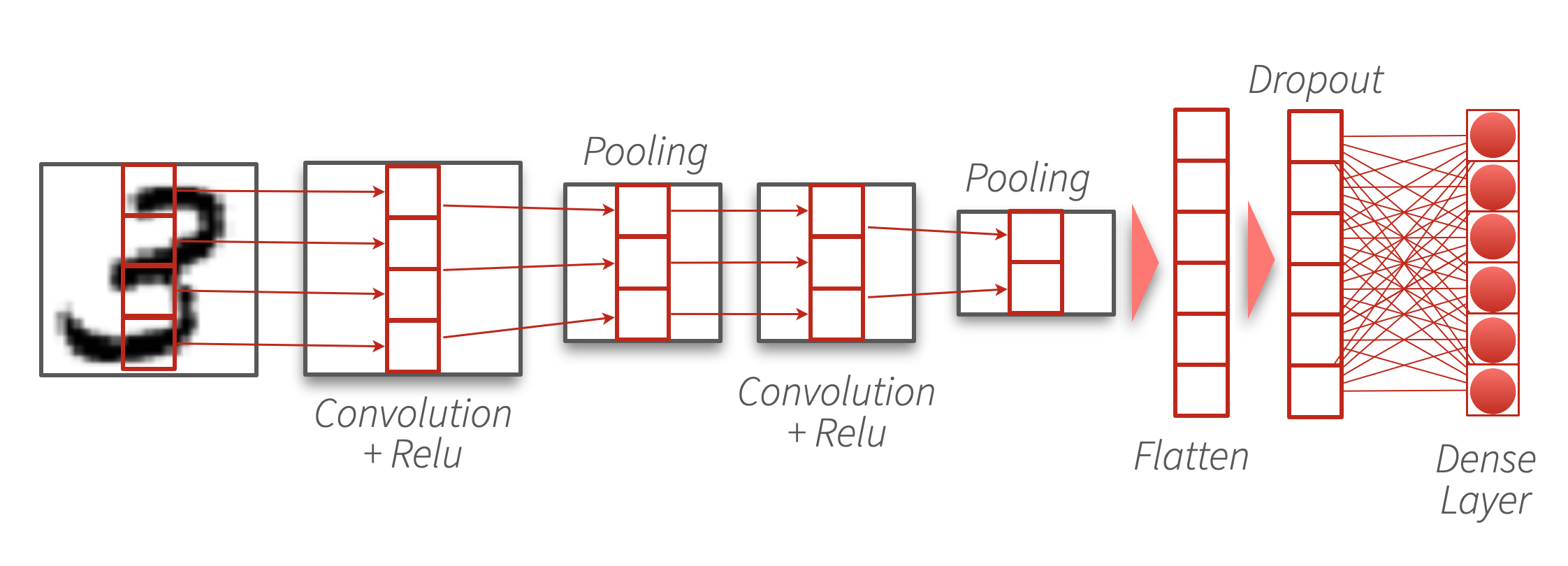
# Define the model and layers
model <- keras_model_sequential(
input_shape = c(28, 28, 1)) |>
layer_conv_2d(
filters = 32, kernel_size = c(3, 3),
activation = "relu") |>
layer_max_pooling_2d(pool_size = c(2, 2)) |>
layer_conv_2d(
filters = 64,
kernel_size = c(3, 3),
activation = "relu") |>
layer_max_pooling_2d(pool_size = c(2, 2)) |>
layer_flatten() |>
layer_dropout(rate = 0.5) |>
layer_dense(units = num_classes, activation = "softmax")
# Inspect the model
summary(model)
plot(model)
# Compile (define loss and optimizer)
model |>
compile(
loss = "categorical_crossentropy",
optimizer = optimizer_rmsprop(),
metrics = c("accuracy")
)
# Fit the model
model |>
fit(
x_train, y_train,
epochs = 30,
batch_size = 128,
validation_split = 0.2
)
# Evaluate and predict
model |>
evaluate(x_test, y_test)
model |>
predict(x_test)
# Save the full model
save_model(model, "mnist-classifier.keras")
# Deploy for serving inference
dir.create("mnist")
export_savedmodel(model, "mnist/1")
rsconnect::deployTFModel("mnist")layer_dense(): A layer connected to all neurons in the preceding layer
layer_einsum_dense(): A dense layer of arbitrary dimensionality
layer_embedding(): Acts as a mapping function, it stores a dense vector for each word in the vocabulary
layer_lambda(): Allows arbitrary expressions to be used as a layer
layer_masking(): Masks a sequence by using a mask value to skip time steps
Layers that create a convolution kernel that is convolved with the layer input over one, two, or three dimensions to produce a tensor of outputs.
layer_conv_1d() / layer_conv_1d_transpose(): Layer of a single dimension (temporal). Transpose does the opposite, deconvolution.
layer_conv_2d() / layer_conv_2d_transpose(): Two dimensional layer (image). Transpose does the opposite, deconvolution.
layer_conv_3d() / layer_conv_3d_transpose(): Three dimensional layer (images over volumes). Transpose does the opposite, deconvolution.
layer_depthwise_conv_1d() / layer_depthwise_conv_2d(): A type of convolution in which each input channel is convolved with a different kernel.
layer_separable_conv_1d() / layer_separable_conv_2d(): A depthwise convolution that acts separately on channels, followed by a pointwise convolution that mixes channels.
layer_depthwise_conv_1d() / layer_depthwise_conv_2d(): A type of convolution in which each input channel is convolved with a different kernel.
layer_separable_conv_1d() / layer_separable_conv_2d() - A depthwise convolution that acts separately on channels, followed by a pointwise convolution that mixes channels.
layer_batch_normalization(): Operates across the batch dimension
layer_layer_normalization(): Operates across the feature dimension
layer_group_normalization(): Operates across channels
layer_spectral_normalization(): Controls the Lipschitz constant of the weights
layer_rms_normalization(): Root Mean Square
layer_batch_normalization(): Maintains the mean output close to 0 and the output standard deviation close to 1.
layer_gaussian_noise(): Layers that randomly “drop” a fraction of input units during training by setting them to 0
layer_dropout(): Non 0 inputs are scaled up
layer_alpha_dropout(): Keeps original mean and variance
layer_gaussian_dropout(): 1-centers Gaussian noise
layer_spatial_dropout_1d() / layer_spatial_dropout_2d() / layer_spatial_dropout_3d(): Drops entire dimensional feature maps instead of individual elements
Layers that reduce each dimension of the input while retaining the most important features
layer_max_pooling_1d() / layer_max_pooling_2d() / layer_max_pooling_3d(): Maximum value over a specified window size (pool size)
layer_average_pooling_1d() / layer_average_pooling_2d() / layer_average_pooling_3d(): Average value over a specified window size (pool size)
layer_global_max_pooling_1d() / layer_global_max_pooling_2d() / layer_global_max_pooling_3d(): Maximum value of the dimension
layer_global_average_pooling_1d() / layer_global_average_pooling_2d() / layer_global_average_pooling_3d(): Average value of the dimension
layer_normalization(): Normalizes continuous features
layer_discretization(): Buckets by ranges
layer_category_encoding(): Encodes integer features
layer_hashing(): Hashes and bins features
layer_hashed_crossing(): Crosses features using the “hashing trick”
layer_string_lookup() / layer_integer_lookup(): Maps a set of arbitrary text or integers via a table-based vocabulary lookup
layer_feature_space(): Main function to specify the how the features are to be pre-processed
feature_float()
feature_float_rescaled()
feature_float_normalized()
feature_float_discretized(num_bins)
feature_integer_categorical()
feature_string_categorical()
adapt(): Calculates the the normalizations, bins, and other conversions against the data set
layer_text_vectorization() / get_vocabulary() / set_vocabulary(): Maps a set of arbitrary text or integers via a table-based vocabulary lookuplayer_mel_spectrogram(): Converts signal to Mellayer_resizing(): Changes the size of images
layer_rescaling(): Multiplies scale by a given number
layer_center_crop(): Crops images to the given size
layer_auto_contrast(): Makes differences between pixels more obvious
layer_aug_mix() |
layer_random_hue() |
layer_cut_mix() |
layer_random_invert() |
layer_mix_up() |
layer_random_rotation() |
layer_solarization() |
layer_random_shear() |
layer_random_contrast() |
layer_random_zoom() |
layer_random_crop() |
layer_random_saturation() |
layer_random_erasing() |
layer_random_sharpness() |
layer_random_flip() |
layer_random_translation() |
layer_random_grayscale() |
layer_random_brightness() |
layer_random_color_jitter() |
layer_random_gaussian_blur() |
layer_random_perspective() |
layer_random_color_degeneration() |
layer_random_posterization() |
text_dataset_from_directory()
audio_dataset_from_directory(): Reads .wav files
image_dataset_from_directory(): This function supports JPEG, Bitmap, PNG and GIF
image_load(): Loads image into a PIL format
image_from_array(): Converts array into PIL format
image_to_array(): Converts PIL image to array
timeseries_dataset_from_array(): Creates a dataset of sliding windows over a time series
pad_sequences(): Pads sequences to the same length
save_model("<path>") / load_model("<path>"): Manage models using the “.keras” file format.
save_model_weights() / load_model_weights(): Manage model weights to/from “.h5” files.
save_model_config() / load_model_config(): Manage model architecture to/from a “.json” file.
export_savedmodel(<model>, "<path>/1"): Save a TF SavedModel for inference.
rsconnect::deployTFModel("<path>")- Deploy a TF SavedModel to Posit Connect for inference.
Introduced in Keras v.3, these are low-level operations that will work the same in JAX, TF and Torch.
op_associative_scan(): Faster op_scan() if the function performs a binary associative operation
op_cast(): Casts to specified dtype
op_cond(): Conditionally applies one of two functions
op_convert_to_array(): Tensor to R array
op_convert_to_numpy(): Tensor to Numpy array
op_convert_to_tensor(): Array to tensor
op_custom_gradient(): Allows fine grained control over the gradients of a sequence for operations.
op_dtype(): Returns tensor’s dtype
op_fori_loop(): For loop, return tensor
op_is_tensor(): Checks for backend specific tensor
op_map(): Applies a function to every single value in the tensor
op_rearrange(): Rearranges tensor to specification
op_scan(): Maps a function, but retaining state
op_scatter(): Modifies tensor in specified locations with zeroes
op_scatter_update(): It modifies tensor in specified locations that do not need to be contiguous
op_searchsorted(): Performs a binary search
op_shape(): Returns tensor’s shape
op_slice(): Extract specific location within the tensor
op_slice_update(): It modifies tensor in a specified location
op_stop_gradient(): Stops gradient computation
op_subset(): Get specific section of the tensor
op_switch(): Applies one of several functions passed to the function based on an index argument
op_unstack(): Splits tensor into a list of tensors separated along the specified axis
op_vectorized_map(): Applies a function to every single value in the tensor. Designed for vectorized operations
op_while_loop(): While loop implementation
op_image_affine_transform(): Applies the given transform
op_image_crop(): Crops to specified height and width
op_image_gaussian_blur(): Applies Gaussian blur
op_image_extract_patches(): Extracts from image
op_image_hsv_to_rgb(): Converts from HSV to RGB
op_image_map_coordinates(): Maps input array to new coordinates by interpolation
op_image_pad(): Pad images with zeroes to specified height and width
op_image_perspective_transform(): Applies a perspective transformation to the image
op_image_resize(): Resize image to size using the specified interpolation method
op_image_rgb_to_grayscale(): Converts from RGB to grayscale
op_image_rgb_to_hsv(): Converts from RGB to HSV
op_average_pool() |
op_batch_normalization() |
op_binary_crossentropy() |
op_celu() |
op_conv() |
op_conv_transpose() |
op_ctc_loss() |
op_depthwise_conv() |
op_elu() |
op_gelu() |
op_glu() |
op_hard_shrink() |
op_hard_sigmoid() |
op_hard_silu() |
op_hard_tanh() |
op_leaky_relu() |
op_log_sigmoid() |
op_log_softmax() |
op_max_pool() |
op_moments() |
op_multi_hot() |
op_categorical_crossentropy() |
op_sparse_categorical_crossentropy() |
op_normalize() |
op_one_hot() |
op_polar() |
op_psnr() |
op_relu() |
op_relu6() |
op_rms_normalization() |
op_selu() |
op_separable_conv() |
op_sigmoid() |
op_silu() |
op_soft_shrink() |
op_softmax() |
op_softplus() |
op_softsign() |
op_sparse_plus() |
op_sparsemax() |
op_squareplus() |
op_tanh_shrink() |
op_threshold() |
op_unravel_index() |
By François Chollet & Tomasz Kalinowski
2025