
Download PDF
Click on R or the Python tab to see the information in your preferred language
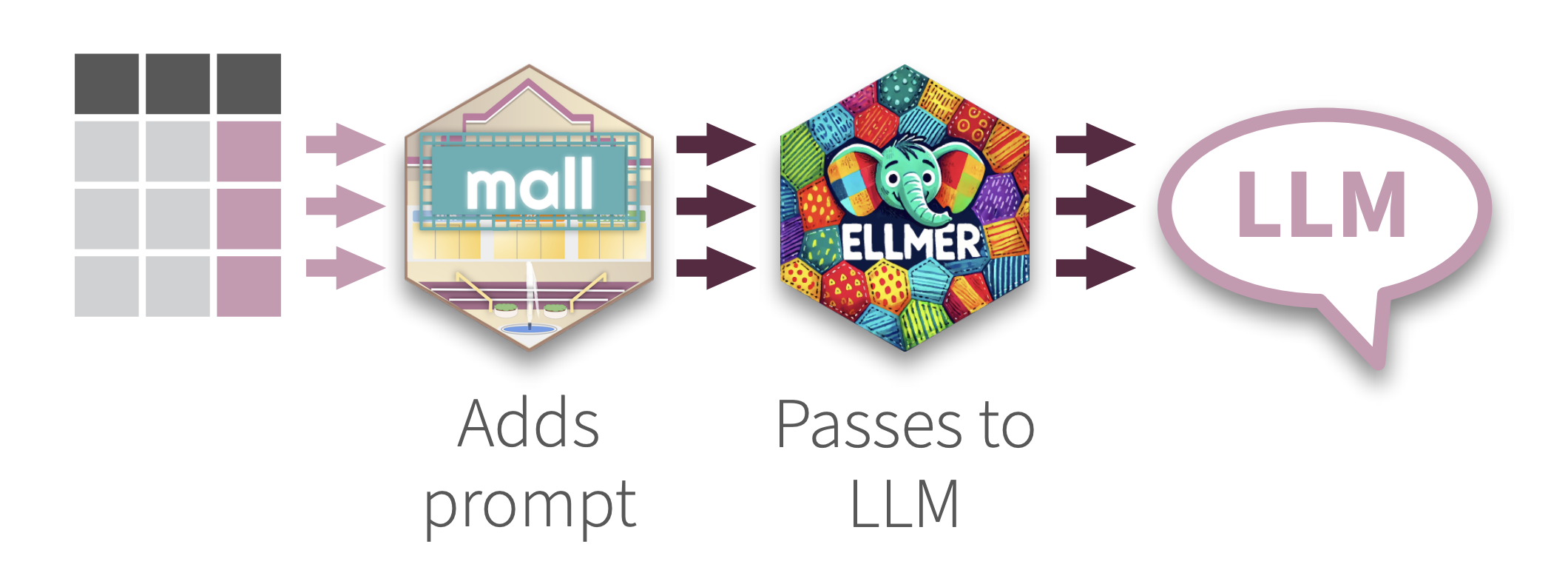
Use LLM’s to perform NLP row-wise over a data frame. mall comes with pre-defined prompts that perform specific NLP operations, and then places the results in a new column. Use OpenAI, Ollama, Anthropic and many others thanks to its integration with ellmer
mall’s data frame functions are designed with ‘tidy’ principals in mind, so they work with the Tidyverse packages. mall also includes functions that work with string vectors.
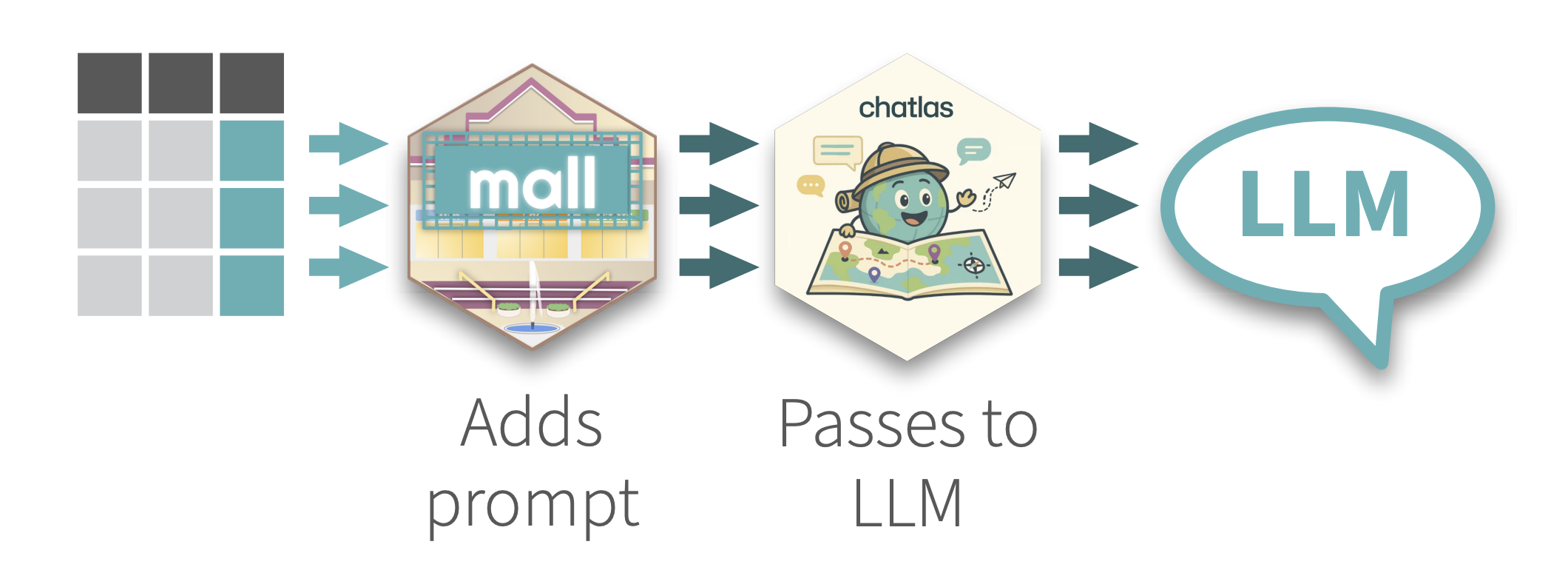
Use LLM’s to perform NLP row-wise over a data frame. mall comes with pre-defined prompts that perform specific NLP operations, and then places the results in a new column. Use OpenAI, Ollama, Anthropic and many others thanks to its integration with chatlas
mall works as an extension for Polars data frames. It also works with string vectors.
Load the libraries
Create a vendor specific chat connection
Pass the chat object to mall
For dataframes:
For vectors:
Connect automatically
As a convenience, mall is able to automatically establish a connection with the LLM. To do this you can use the .mall_chat option: options(.mall_chat=ellmer::chat_openai(model="gpt-4o")) Add this line to your .Rprofile file in order for that code to run every time you start R. You can call usethis::edit_r_profile() to edit.
Start by creating a new LLM connection
For Dataframes
Load the library
Read or load your data frame
Pass the chat object to mall
Access NLP functions via .llm
For String vectors
Load the LLMVec class
Create a new LLMVec object
Pass a vector to a function in the new object
llm_sentiment(.data, col, options = c("positive", "negative", “neutral"), pred_name = “.sentiment", additional_prompt = “”)
llm_vec_sentiment(x, options = c("positive", "negative", "neutral"), additional_prompt = "", preview = FALSE)
Special arguments:
options: Customize the sentiments to check for: options = c(“positive”, “negative”). Use ‘tilde’ to mask the results, for example c("positive" ~ 1, "negative" ~ 0)) returns 1 for positive and 0 for negative.
<Dataframe>.llm.sentiment(col, options = ['positive', 'negative', 'neutral'], additional='', pred_name ='sentiment')
<LLMVec object>.sentiment(x, options=['positive', 'negative', 'neutral'], additional='')
Special arguments:
options: Customize the sentiments to check for: options = ["positive", "negative"]. Use a DICT object to mask the results, for example {"positive": 1, "negative" 0} returns 1 for positive and 0 for negative.
Extract specific entity, or entities, from the provided text
llm_extract(.data, col, labels, expand_cols = FALSE, additional_prompt = "", pred_name = “.extract")
llm_vec_extract(x, labels = c(), additional_prompt = "", preview = FALSE)
Special arguments
labels: A vector to specify the entities to identify expand_cols - If multiple labels, this indicates if the labels will show up in their own column (data frames only)
<DataFrame>.llm.extract(col, labels='', expand_cols = False, additional = '', pred_name = 'extract')
<LLMVec object>.extract(x, labels='', additional='')
Special arguments
labels: A vector to specify the entities to identify expand_cols - If multiple labels, this indicates if the labels will show up in their own column (data frames only)
Summarize text into a specified number of words
llm_summarize( .data, col, max_words = 10, pred_name = ".summary", additional_prompt = "")
llm_vec_summarize(x, max_words = 10, additional_prompt = "", preview = FALSE)
Check if a statement is true or not based on the provided text
llm_verify(.data, col, what, yes_no = factor(c(1, 0)), pred_name = ".verify", additional_prompt = "")
llm_vec_verify(x, what, yes_no = factor(c(1, 0)), additional_prompt = “", preview = FALSE)
Special arguments
yes_no: Customize what it returns for true/false with a vector yes_no = c("y", "n").
<DataFrame>.llm.verify(col, what='', yes_no=[1, 0], additional='', pred_name='verify')
<LLMVec object>.verify(x, what='', yes_no=[1, 0], additional='')
Special arguments
yes_no: Customize what it returns for true/false with a vector yes_no = ["y", "n"].
Classify the provided text as one of the options provided via the labels
llm_classify(.data, col, labels, pred_name = ".classify", additional_prompt = "")
llm_vec_classify(x, labels, additional_prompt = "", preview = FALSE)
Special arguments
labels: A character vector with at least 2 labels to classify the text as
<DataFrame>.llm.classify(col, labels='', additional='', pred_name='classify')
<LLMVec object>.classify(x, labels='', additional='')
Special arguments
labels: A character vector with at least 2 labels to classify the text as
Translate into target language
llm_translate( .data, col, language, pred_name = ".translation", additional_prompt = “")
llm_vec_translate(x, language, additional_prompt = "", preview = FALSE)
Special arguments
language: Target language. No origin language is passed since the LLM detects it automatically.
<DataFrame>.llm.translate(col, language='', additional='', pred_name='translation')
<LLMVec object>.translate(x, language='', additional='')
Special arguments
language: Target language. No origin language is passed since the LLM detects it automatically.
Create your own prompt
llm_custom(.data, col, prompt = "", pred_name = ".pred", valid_resps = "")
llm_vec_custom(x, prompt = "", valid_resps = NULL)
Special arguments
valid_resps: A vector to specify the set of answers expected back. mall will change those not in the set to NA
<DataFrame>.llm.custom(col, prompt='', valid_resps='', pred_name='custom')
<LLMVec object>.custom(x, prompt='', valid_resps='')
Special arguments
valid_resps: A vector to specify the set of answers expected back.
additional_prompt: Appends instructions to the LLM.
pred_name: Name of the new column. Defaults are set based on the NLP operation. (Data frames only)
preview: Returns what it would be sent to the LLM instead (Vectors only)
If Ollama is the only LLM provider you are using, then a simplified way to connect is available which does not require an ellmer Chat object. Simply pass “ollama” as the backend, and specify the model:
By default, mall saves the LLM results in a temp folder. To specify a folder call:
To turn off use: